What is an API Gateway?
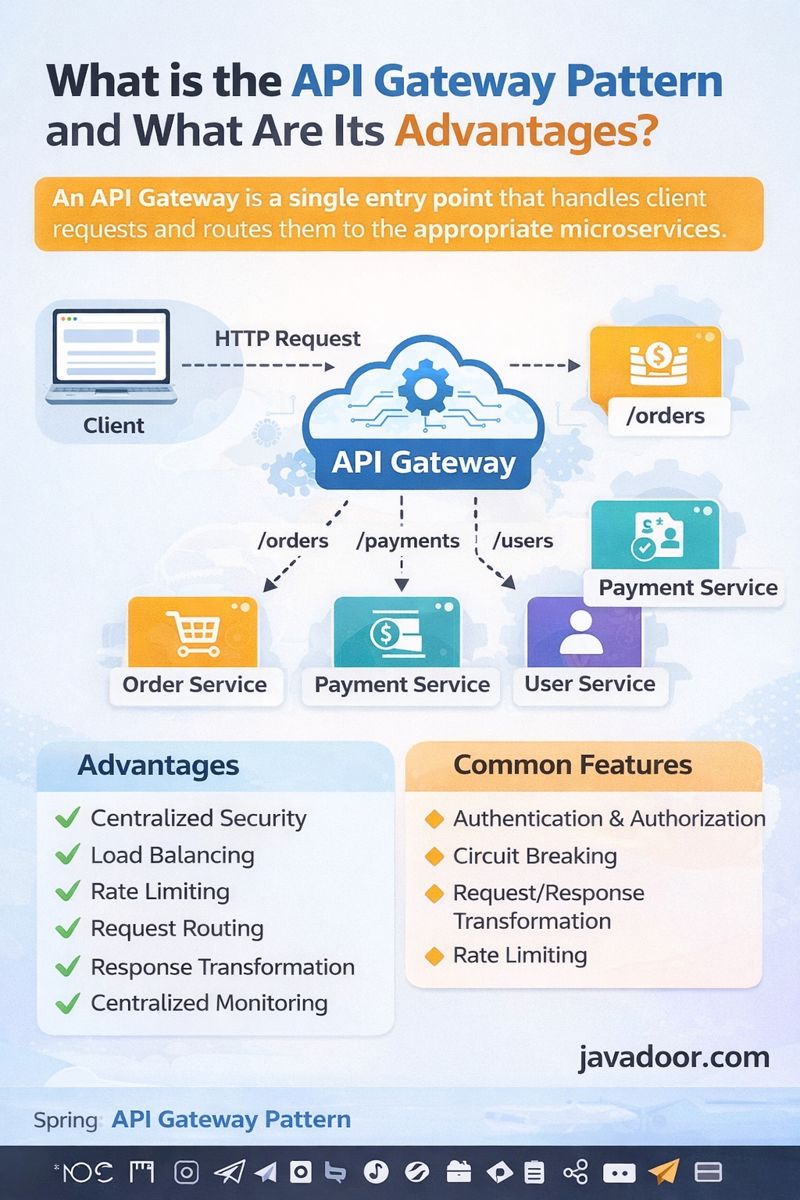
An API Gateway is a single entry point for all client requests in a microservices architecture.
Instead of clients calling multiple microservices directly, they call the API Gateway, which then routes the request to the appropriate backend service.
🔹 Why Do We Need an API Gateway?
Without an API Gateway:
-
Clients must know the location of every microservice
-
Security, logging, and validation logic gets duplicated
-
Changes in backend services affect clients
👉 API Gateway solves all of this.
🔹 Core Responsibilities of an API Gateway
-
Request Routing
-
Routes requests to correct microservice
-
/orders → Order Service
-
-
Authentication & Authorization
-
JWT validation
-
OAuth2 handling
-
Role-based access control
-
-
Rate Limiting
-
Prevents abuse (e.g., 100 req/min per user)
-
-
Load Balancing
-
Distributes traffic among service instances
-
-
Request/Response Transformation
-
Modify headers or payloads
-
-
Centralized Logging & Monitoring
-
Circuit Breaking & Resilience
-
Prevents cascading failures
-
🔹 Popular API Gateways
-
Spring Cloud Gateway
-
Netflix Zuul (older)
-
Kong
-
NGINX
-
AWS API Gateway
🔹 Example Architecture
Client
⬇
API Gateway
⬇
Order Service
Payment Service
User Service
🔹 Example (Spring Cloud Gateway Route)
🔹 Advantages of API Gateway
✅ Centralized security
✅ Simplifies client-side logic
✅ Improves performance
✅ Enables microservice scalability
✅ Hides internal service structure
🔹 Drawbacks
❌ Single point of failure (if not HA)
❌ Can become performance bottleneck
❌ Adds operational complexity
