What is Event-Driven Architecture (EDA)?
In Event-Driven Architecture, services:
-
Produce events when something happens
-
Consume events asynchronously
-
Do not wait for each other
👉 Services are loosely coupled.
📌 Example Event:
🔹 Why Use Event-Driven Architecture?
Without EDA:
-
Services call each other synchronously
-
Failures propagate
-
Poor scalability
With EDA:
-
High throughput
-
Fault tolerance
-
Better scalability
🔹 Role of Kafka in Microservices
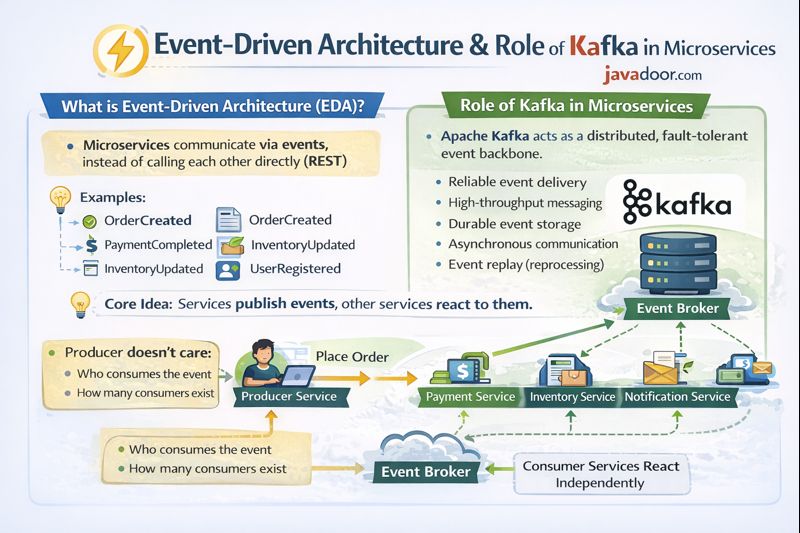
Apache Kafka is a distributed event-streaming platform.
Kafka acts as:
-
Event broker
-
Message buffer
-
Streaming platform
🔹 Kafka Core Concepts
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Topic | Event category |
| Partition | Parallelism |
| Producer | Publishes events |
| Consumer | Reads events |
| Consumer Group | Scales consumers |
| Offset | Message position |
🔹 Kafka Event Flow
-
Producer publishes event to topic
-
Kafka stores event durably
-
Consumers read at their own pace
-
Offset committed after processing
🔹 Why Kafka is Preferred?
✅ High throughput
✅ Horizontal scalability
✅ Message durability
✅ Replay capability
✅ Loose coupling
🔹 Example (E-commerce)
Order Service → publishes OrderPlaced
Payment Service → consumes
Email Service → consumes
Inventory Service → consumes
👉 No direct dependency.
🔹 Kafka Delivery Semantics
-
At-most-once
-
At-least-once
-
Exactly-once
🔹 Kafka vs RabbitMQ (Quick)
| Feature | Kafka | RabbitMQ |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | Very High | Medium |
| Retention | Long | Short |
| Replay | Yes | No |
| Use Case | Event streams | Task queues |
⭐ Interview One-Liner
“Event-driven architecture uses events for communication, and Kafka enables scalable, fault-tolerant, asynchronous messaging between microservices.”
🔹 Common Follow-Up Questions
-
How do you handle duplicate events?
-
How do you ensure ordering in Kafka?
-
What is consumer lag?
