JWT (JSON Web Token) – Complete Notes
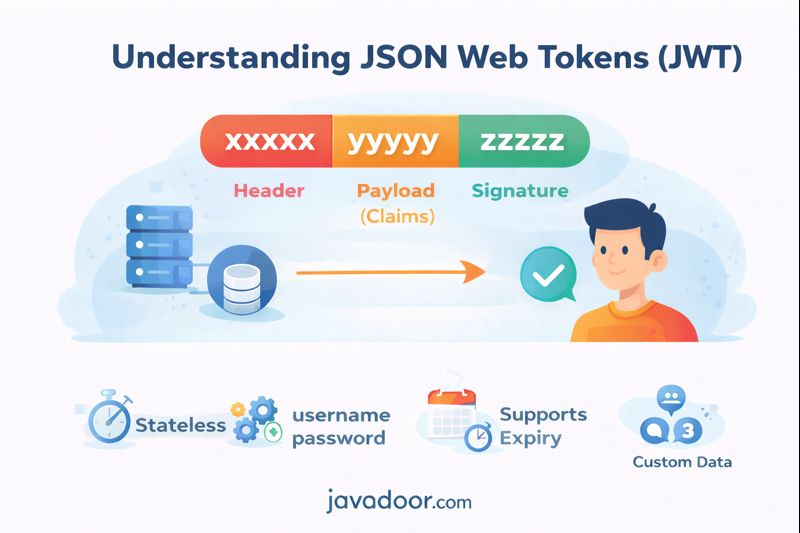
What is JWT?
JWT (JSON Web Token) is a stateless authentication mechanism used to securely transmit information between parties as a JSON object.
It is digitally signed using:
- HMAC (symmetric key) or
- RSA (public/private key pair)
So the data can be verified and trusted.
Key Advantages of JWT
1. Compact
JWT is small in size and can be easily sent in:
Authorization: Bearer <token>
Which makes it fast and network efficient.
2. Stateless (Self-contained)
JWT contains all required user information.
Server does not need to query database on every request.
3. Supports Expiry
JWT has built-in expiry using:
exp (expiration time)
4. Supports Custom Data
You can add:
- userId
- roles
- permissions
inside JWT claims.
Where is JWT Used?
JWT is commonly used for:
- Authentication – verifying user identity
- Authorization – checking permissions
- SSO (Single Sign-On) – login once, access multiple apps
JWT Authentication Flow
From Page 1 diagram:
- Client logs in with username/password
- Authentication server generates JWT
- Client stores token
- Client sends token in every request
- Resource server validates JWT
- Response returned to client
Old Method: Session-Based Authentication (JSESSIONID)
From Page 2:
Flow:
- User logs in
- Server creates session
- Session ID stored in DB
- Cookie sent to client
- Every request → DB lookup
Disadvantages:
- Stateful
- DB dependency
- Not scalable
- Problem in distributed systems
JWT Structure
JWT has 3 parts:
xxxxx.yyyyy.zzzzz
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Header | Token type & algorithm |
| Payload | User data (claims) |
| Signature | Digital signature |
JWT Header Example
{
"typ": "JWT",
"alg": "RS256"
}
Contains:
- Token type
- Algorithm used (RSA / HMAC)
JWT Payload (Claims)
Payload stores user data.
Registered Claims (Standard)
| Claim | Meaning |
|---|---|
| iss | Issuer |
| sub | Subject (user) |
| aud | Audience |
| exp | Expiry time |
| iat | Issued at |
| jti | Unique token id |
Public Claims
Custom but shared across systems.
Private Claims
Custom and internal to your system.
JWT Signature Creation
Steps:
- Base64 encode Header
- Base64 encode Payload
- Join with dot
- Sign using RSA or HMAC
- Append signature
This ensures:
- Token integrity
- Token authenticity
Sample API Request
From Page 3:
curl --location --request GET "https://exampleHost.com/api/resource" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIs..."
Challenges with JWT
1. Token Invalidation Problem
If user is blocked:
- Token still valid until expiry
Solutions:
- Maintain blacklist in DB/Redis
- Use short-lived tokens
- Use token once (OTP style)
2. JWT is Encoded, Not Encrypted
Anyone can decode payload.
Solution:
- Use JWE (JSON Web Encryption)
- Encrypt payload data
3. alg = none Attack
Some attackers send:
"alg": "none"
This disables signature.
Such tokens must be rejected.
4. JWK Exploit
Never trust public key sent inside token.
Always fetch keys from:
https://auth-server/.well-known/jwks.json
Use kid to select correct key.
Interview Questions & Answers
Q1. Is JWT encrypted?
No. JWT is only Base64 encoded, not encrypted.
Q2. Why JWT is called stateless?
Because server does not store any session.
Q3. Where is user data stored in JWT?
Inside payload (claims).
Q4. What happens when JWT expires?
Client must re-authenticate.
Q5. Can JWT be revoked?
Not directly. You need:
- blacklist
- short expiry
- refresh tokens
Q6. Difference between Session and JWT?
| Session | JWT |
|---|---|
| Stateful | Stateless |
| DB lookup | No DB |
| Cookie | Authorization header |
| Not scalable | Highly scalable |
Q7. Why JWT is preferred in microservices?
Because:
- No shared session
- No central DB
- Works across services
Final Summary
JWT is:
✔ Stateless
✔ Scalable
✔ Perfect for APIs
✔ Ideal for microservices
But has challenges:
❌ No easy logout
❌ Token revocation hard
❌ Payload visible
So best practice:
Use short expiry + refresh tokens + HTTPS + JWE (if needed)
JWT is not just an authentication method –
it is the foundation of modern API security.
