1️⃣ Servlet and Servlet Container
🔹 What is a Servlet?
- A Servlet is a Java class that handles HTTP requests and generates HTTP responses.
- It acts as a bridge between client and server.
- Used mainly for building web applications.
Key Responsibilities:
- Accept client request
- Process business logic
- Generate response (HTML / JSON / XML)
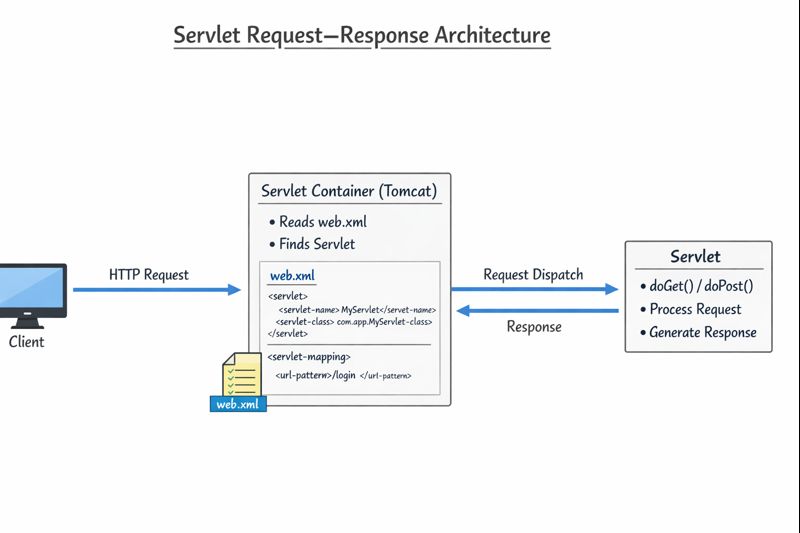
🔹 What is a Servlet Container?
- A Servlet Container manages the lifecycle of servlets.
- Examples:
- Tomcat
- Jetty
- WebLogic
Responsibilities:
- Create servlet instances
- Manage lifecycle (
init,service,destroy) - Handle threading
- Map URLs to servlets using
web.xmlor annotations
🔹 Request–Response Flow
- Client sends HTTP request
- Request reaches Servlet Container (Tomcat)
- Container checks web.xml
- Identifies mapped servlet
- Invokes servlet
- Servlet processes and returns response
🔹 Servlet Example
public class DemoServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
String path = request.getPathInfo();
if ("/firstendpoint".equals(path)) {
// logic
}
}
}
🔹 web.xml Mapping
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DemoServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>DemoServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DemoServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/demo/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
✅ Quick Summary
- Servlet handles request/response
- Servlet Container manages lifecycle
web.xmlmaps URLs to servlets- Tight coupling and manual configuration
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- What is a Servlet Container?
- Explain servlet lifecycle.
- Role of
web.xml? - Difference between
doGet()anddoPost()?
2️⃣ Problems with Traditional Servlets
🔸 Major Challenges
- ❌ Too much XML configuration
- ❌ Tight coupling
- ❌ Difficult unit testing
- ❌ Hard REST API management
- ❌ No built-in integration support
✅ Quick Summary
- Servlets are low-level
- Not scalable for large apps
- Spring solves these issues
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- Why are Servlets not preferred today?
- What makes Servlets tightly coupled?
- Why is testing difficult in Servlets?
3️⃣ Spring Framework Introduction
🔹 What is Spring Framework?
- A lightweight Java framework
- Solves problems of Servlets
- Based on Inversion of Control (IoC)
🔹 Core Features
- Dependency Injection
- Loose coupling
- Annotation-based configuration
- Spring MVC
- Easy integration
✅ Quick Summary
- Spring simplifies Java enterprise apps
- Promotes clean architecture
- Enables easy testing
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- What is Spring Framework?
- Advantages of Spring?
- Why Spring is lightweight?
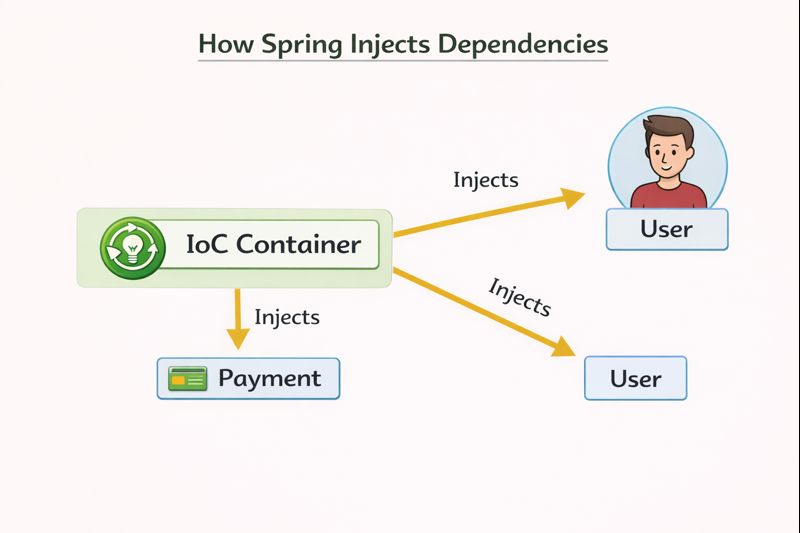
4️⃣ Dependency Injection (IoC)
🔹 Without Dependency Injection
public class Payment {
User sender = new User(); // tight coupling
}
Problems:
- ❌ Tight coupling
- ❌ Cannot mock
- ❌ Hard to extend
🔹 With Dependency Injection
@Component
public class Payment {
@Autowired
User sender;
}
🔹 Key Annotations
- @Component → Bean creation
- @Autowired → Inject dependency
🔹 Internal Working
- Spring scans classes
- Creates beans
- Resolves dependencies
- Injects at runtime
🔹 Best Practices
- Prefer constructor injection
- Avoid field injection in production
- Use interfaces
✅ Quick Summary
- DI removes tight coupling
- Improves testability
- Managed by Spring IoC container
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- What is Dependency Injection?
- Difference between IoC and DI?
- Types of DI in Spring?
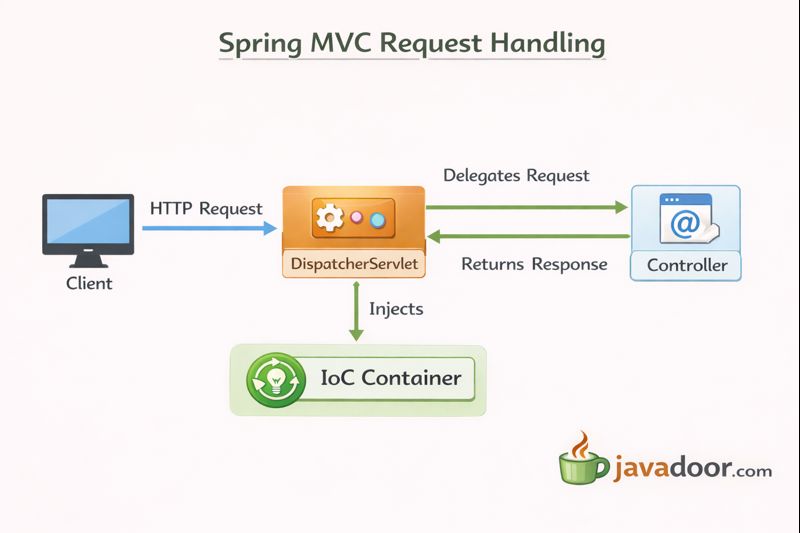
5️⃣ Spring MVC & DispatcherServlet
🔹 What is DispatcherServlet?
- Front Controller in Spring MVC
- Handles all incoming requests
🔹 Request Flow
- Request hits DispatcherServlet
- HandlerMapping identifies controller
- Controller method invoked
- Response returned
🔹 Controller Example
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/payment")
public class PaymentController {
@GetMapping("/details")
public String getDetails() {
return "details";
}
}
✅ Quick Summary
- DispatcherServlet is central controller
- Clean separation of concerns
- Supports REST APIs
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- What is DispatcherServlet?
- Role of HandlerMapping?
- Difference between Controller & RestController?
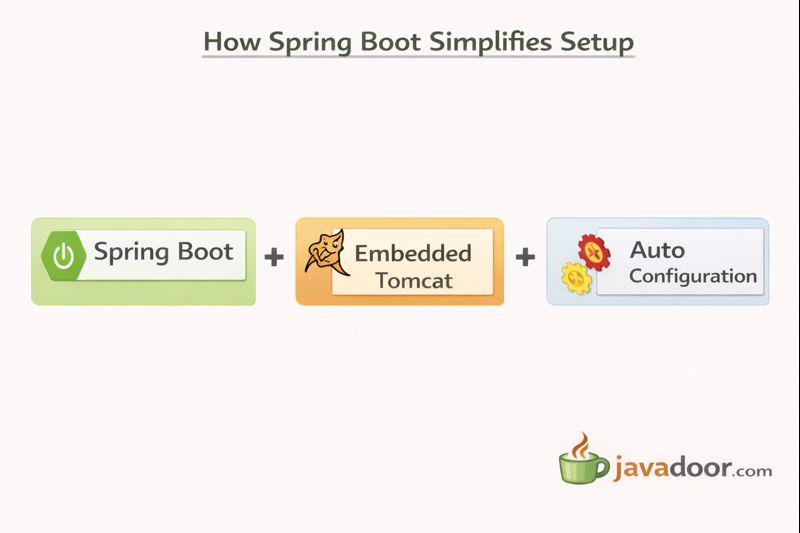
6️⃣ Spring Boot Introduction
🔹 What is Spring Boot?
- Built on top of Spring Framework
- Used to create production-ready apps quickly
🔹 Problems Solved by Spring Boot
- Dependency management
- Configuration complexity
- Server setup
🔹 Key Features
- Auto Configuration
- Embedded Server
- Starter Dependencies
- Convention over Configuration
🔹 Main Class
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
🔹 Embedded Server
- No WAR file
- No external Tomcat
- Just run
main()method
🔹 REST API Example
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/myapi")
public class MyController {
@GetMapping("/firstapi")
public String getData() {
return "Hello from concept and coding";
}
}
✅ Quick Summary
- Spring Boot accelerates development
- Reduces configuration
- Embedded server support
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- Difference between Spring & Spring Boot?
- What is Auto Configuration?
- What is Embedded Server?
📌 FINAL CONCLUSION
- Servlets are foundation but limited
- Spring introduces IoC and MVC
- Spring Boot makes Spring production-ready
- Ideal for microservices & REST APIs