🌱 Spring Boot – @Transactional (Complete Notes)
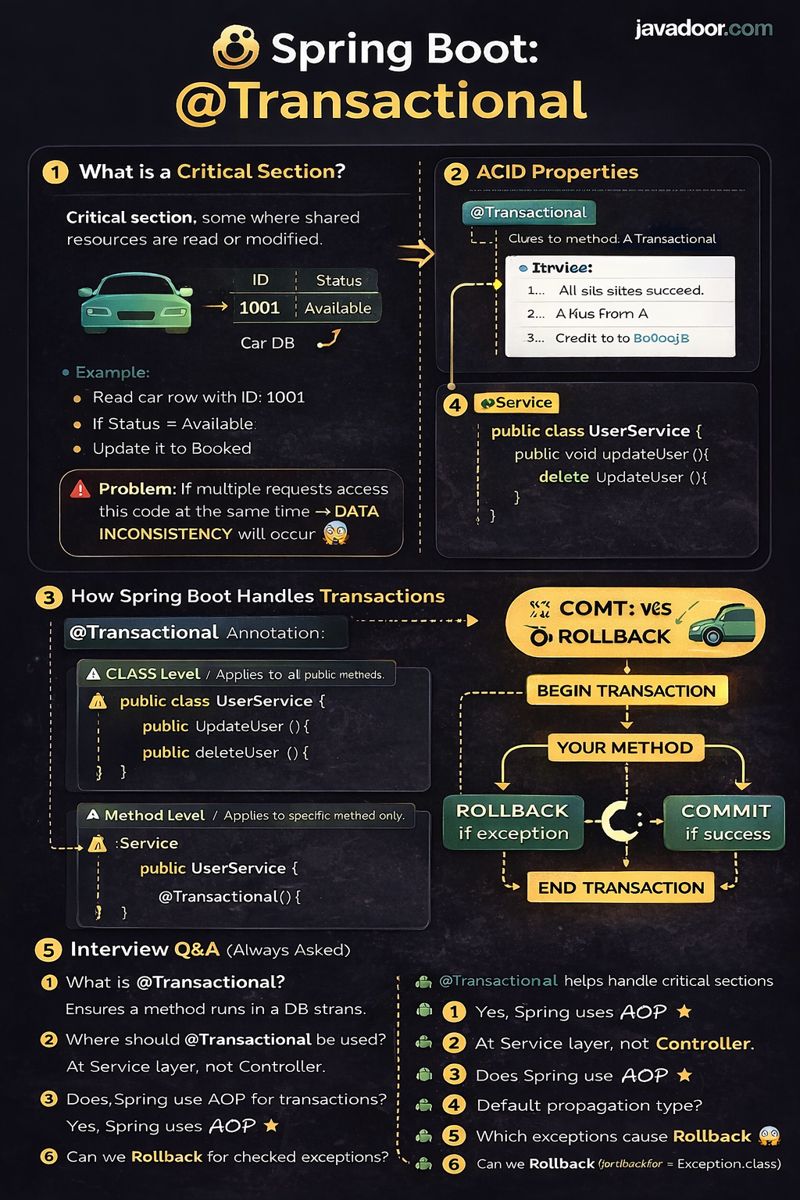
1️⃣ What is a Critical Section?
A Critical Section is a block of code where shared resources (like database rows) are read or modified.
Example (from PDF – Car Booking)
- Read car row with ID =
1001 - If status =
Available - Update status to
Booked
📌 Problem:
If multiple requests access this code at the same time → Data inconsistency may occur.
✔ Solution: Use TRANSACTIONS
2️⃣ Why Do We Need Transactions?
Transactions ensure safe execution of critical code by maintaining ACID properties.
3️⃣ ACID Properties (Very Important)
🔹 A – Atomicity
- Either all operations succeed or none
- If any step fails → Rollback
📌 Example:
Debit A
Credit B
If Credit fails → Debit is rolled back
🔹 C – Consistency
- Database must remain valid before and after the transaction
- No partial or corrupt data
🔹 I – Isolation
- Multiple transactions can run in parallel
- They do not interfere with each other
📌 Prevents dirty reads, phantom reads, etc.
🔹 D – Durability
- Once committed, data will never be lost
- Even after crash or power failure
4️⃣ Transaction Flow (Logical)
BEGIN TRANSACTION
Debit from A
Credit to B
IF success
COMMIT
ELSE
ROLLBACK
END TRANSACTION
5️⃣ How Spring Boot Handles Transactions
Spring Boot provides declarative transaction management using:
@Transactional
6️⃣ Required Dependencies (Relational DB)
🔹 Spring Data JPA
Helps interact with relational databases without writing boilerplate code
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
✔ Database driver dependency is also required (MySQL, Oracle, etc.)
7️⃣ Enabling Transaction Management
In Spring Boot, it is auto-configured, but can be explicitly enabled:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
8️⃣ @Transactional Placement
🔹 At Class Level
- Applies to all public methods
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
public void updateUser() {}
public void deleteUser() {}
}
🔹 At Method Level
- Applies to specific method only
@Service
public class UserService {
@Transactional
public void updateUser() {}
}
📌 Best Practice:
Use @Transactional at Service layer, not Controller.
9️⃣ Transaction Management Uses AOP
Spring uses AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming) internally.
How it Works:
- A Pointcut finds methods annotated with
@Transactional - An Around Advice wraps the method
- Calls
invokeWithinTransaction()fromTransactionInterceptor
✔ This is why internal method calls don’t trigger transactions.
🔟 Real Code Flow (From PDF)
Controller
@GetMapping("/updateuser")
public String updateUser() {
user.updateUser();
return "user updated successfully";
}
Service / Component
@Component
public class User {
@Transactional
public void updateUser() {
System.out.println("UPDATE QUERY TO update the user db values");
}
}
📌 If any exception occurs:
- ❌ Transaction → ROLLBACK
- ✔ If success → COMMIT
1️⃣1️⃣ What Happens Internally?
- Transaction starts before method execution
- Your business logic runs
- If exception → rollback
- If no exception → commit
1️⃣2️⃣ Topics Mentioned for Next Level (From PDF)
🔹 Transaction Context
🔹 Transaction Manager
- Programmatic
- Declarative
🔹 Propagation Types
- REQUIRED
- REQUIRES_NEW
- SUPPORTS
- NOT_SUPPORTED
- MANDATORY
- NEVER
- NESTED
🔹 Isolation Levels
- READ_UNCOMMITTED
- READ_COMMITTED
- REPEATABLE_READ
- SERIALIZABLE
🔹 Transaction Timeout
❓ Interview Questions & Answers
Q1. What is @Transactional?
Answer:
It ensures that a method executes within a database transaction, maintaining ACID properties.
Q2. What happens if an exception occurs?
Answer:
Spring performs a ROLLBACK if a runtime exception occurs.
Q3. Where should @Transactional be used?
Answer:
At the Service layer, not Controller.
Q4. Does Spring use AOP for transactions?
Answer:
Yes, Spring uses AOP with proxy-based interception.
Q5. Why internal method calls don’t work with @Transactional?
Answer:
Because they bypass the Spring proxy.
Q6. Default propagation type?
Answer:
REQUIRED
Q7. Which exceptions cause rollback?
Answer:
RuntimeException and Error (by default)
Q8. Can we rollback for checked exceptions?
Answer:
Yes, using:
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
✅ Summary (One-Line)
@Transactional ensures safe, consistent, and reliable database operations using AOP-based transaction management.
