🌱 Spring Boot – @Profile
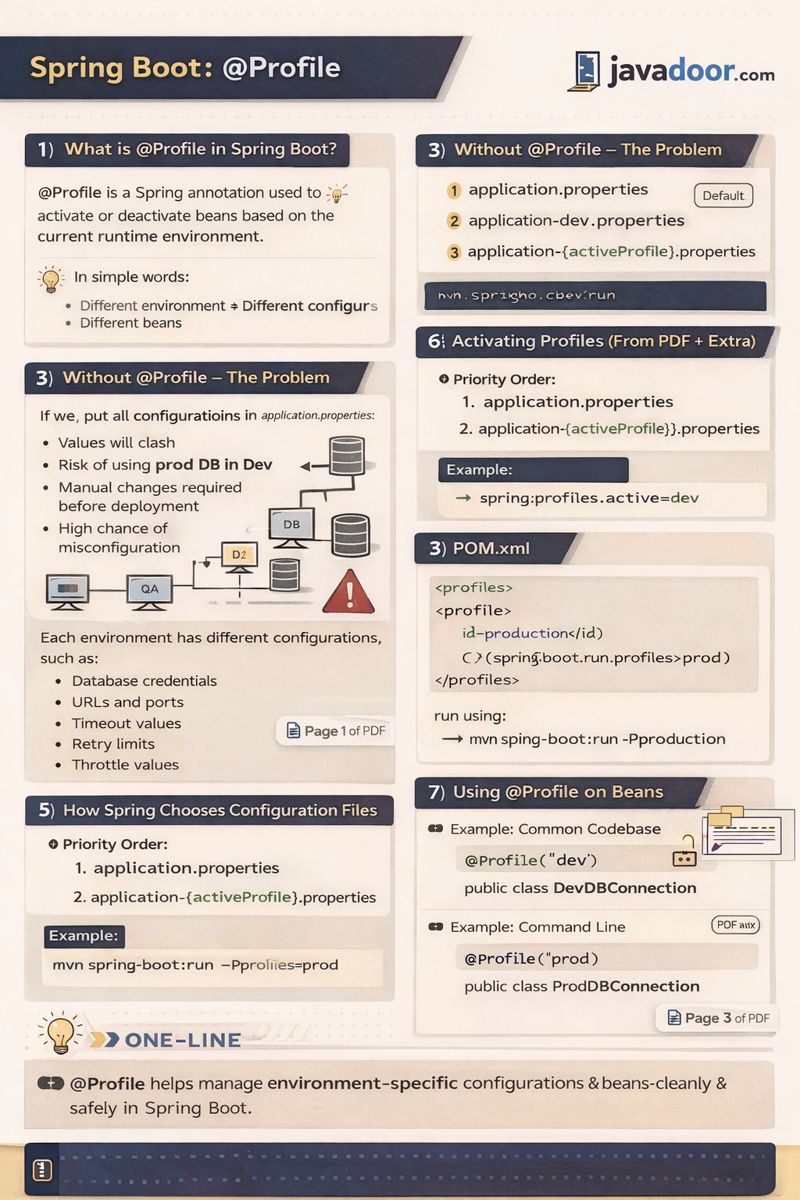
1️⃣ What is @Profile in Spring Boot?
@Profile is a Spring annotation used to activate or deactivate beans based on the current runtime environment.
👉 In simple words:
Different environments → Different configurations → Different beans
2️⃣ Why Do We Need @Profile? (Problem Statement)
In real-world applications, we usually have multiple environments:
| Environment | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Dev / Local | Development |
| QA / Stage | Testing |
| Prod | Live users |
Each environment has different configurations, such as:
- Database credentials
- URLs and ports
- Timeout values
- Retry limits
- Throttle values
📌 As shown on Page 1 of the PDF,
Dev, QA, and Prod machines all connect to different databases with different credentials.
3️⃣ Without @Profile – The Problem
❌ If we put all configurations in application.properties:
- Values will clash
- Risk of using prod DB in dev
- Manual changes required before deployment
- High chance of misconfiguration
4️⃣ Profiling Concept (Core Idea)
Spring Boot supports profile-based configuration files:
application.properties (default)
application-dev.properties
application-qa.properties
application-prod.properties
📌 Only one or more profiles are activated at runtime.
5️⃣ How Spring Chooses Configuration Files
Priority Order:
application.propertiesapplication-{activeProfile}.properties
Example:
spring.profiles.active=dev
✔ Spring loads:
application.propertiesapplication-dev.properties
6️⃣ Activating Profiles (From PDF + Extra)
✅ Method 1: application.properties
spring.profiles.active=qa
✅ Method 2: Command Line
mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=prod
✅ Method 3: POM.xml
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>production</id>
<properties>
<spring-boot.run.profiles>prod</spring-boot.run.profiles>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
Run using:
mvn spring-boot:run -Pproduction
7️⃣ Using @Profile on Beans
Example: Common Codebase, Different Beans
@Component
@Profile("dev")
public class DevDBConnection {
}
@Component
@Profile("prod")
public class ProdDBConnection {
}
✔ Only matching profile bean is created.
8️⃣ Multiple Profiles at Once (From PDF)
spring.profiles.active=dev,qa
✔ Beans with:
@Profile("dev")@Profile("qa")
are both loaded.
9️⃣ Common Codebase – Multiple Applications Use Case
📌 PDF Scenario (Page 3):
- 2 applications
- Same codebase
- Bean should be created only for one application
Solution:
@Component
@Profile("app1")
public class App1SpecificBean {
}
✔ Bean is created only when app1 profile is active.
🔟 Difference: @Profile vs @ConditionalOnProperty
| Feature | @Profile | @ConditionalOnProperty |
|---|---|---|
| Based On | Environment | Property value |
| Use Case | Dev / QA / Prod | Feature toggle |
| Flexibility | Medium | High |
| Complexity | Low | Medium |
1️⃣1️⃣ Advantages of @Profile
✅ Clean environment separation
✅ Avoids accidental prod usage
✅ Easy deployment configuration
✅ Works well with CI/CD
✅ Reduces manual changes
1️⃣2️⃣ Disadvantages of @Profile
❌ Hardcoded environment names
❌ Too many profiles can confuse
❌ Not ideal for feature toggles
❌ Needs proper documentation
1️⃣3️⃣ Best Practices (Added)
✔ Use profiles mainly for environment differences
✔ Avoid putting business logic behind profiles
✔ Log active profiles at startup
✔ Combine with @ConditionalOnProperty if needed
✔ Never store secrets in Git
🧠 Interview Questions & Answers
Q1️⃣ What is @Profile in Spring Boot?
Answer:
@Profile is used to enable or disable beans based on the active environment profile.
Q2️⃣ Where do we define active profiles?
Answer:
application.properties- Command line
- JVM arguments
- POM.xml
Q3️⃣ Can we activate multiple profiles?
Answer:
Yes, using comma-separated values.
Q4️⃣ Difference between @Profile and @ConditionalOnProperty?
Answer:
@Profile is environment-based, while @ConditionalOnProperty is configuration-value based.
Q5️⃣ What happens if no profile is active?
Answer:
Only application.properties is loaded.
Q6️⃣ Is @Profile evaluated at runtime?
Answer:
No, it is evaluated during application startup.
Q7️⃣ Can we apply @Profile on @Configuration classes?
Answer:
Yes, both on beans and configuration classes.
Q8️⃣ Real-world use of @Profile?
Answer:
Different DBs, APIs, credentials, logging levels per environment.
📌 One-Line Summary
@Profilehelps manage environment-specific configurations and beans cleanly and safely in Spring Boot.
