🌱 Spring Boot – Dynamic Bean Initialization
1️⃣ What is Dynamic Bean Initialization?
Dynamic Bean Initialization means deciding which bean implementation should be created at runtime, based on:
- Configuration values
- Conditions
- Properties
- Environment variables
👉 Instead of fixing the bean at compile time, Spring decides dynamically during startup.
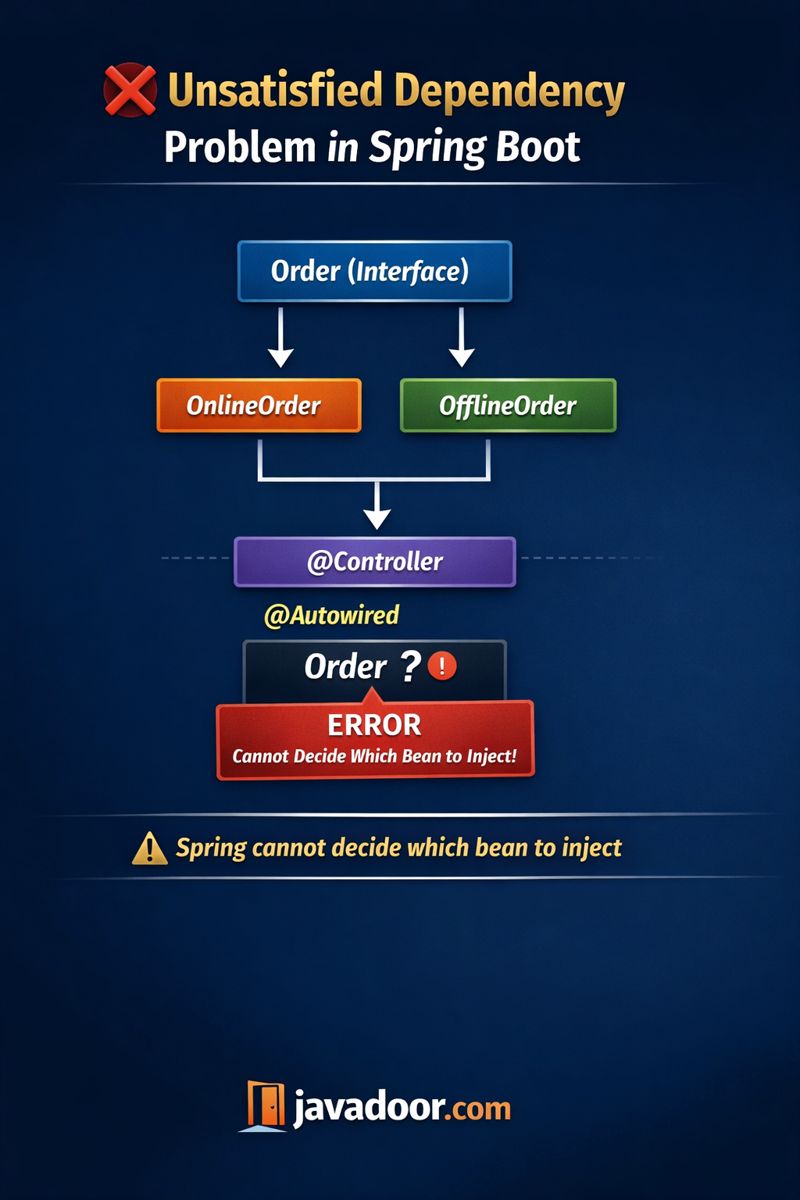
2️⃣ Problem: Unsatisfied Dependency
🔴 Scenario Explained
- You have an interface (e.g.,
Order) - Multiple implementations exist:
OnlineOrderOfflineOrder
- Spring does not know which one to inject
❌ Error Seen
UnsatisfiedDependencyException:
Error creating bean with name 'user'
❓ Why this happens
- Spring finds more than one bean of the same interface
- No clear instruction is provided to choose one
3️⃣ Example Structure (From PDF – Page 1)
Interface
public interface Order {
void createOrder();
}
Implementations
@Component
public class OnlineOrder implements Order {
public void createOrder() {
System.out.println("Created Online Order");
}
}
@Component
public class OfflineOrder implements Order {
public void createOrder() {
System.out.println("Created Offline Order");
}
}
Controller
@Autowired
Order order;
❌ Result: Spring fails because it finds two beans of type Order
4️⃣ Solution 1: Using @Qualifier
✅ What is @Qualifier?
@Qualifier tells Spring exactly which bean to inject.
✔ Example
@Autowired
@Qualifier("onlineOrder")
Order order;
✔ Result
- Spring injects
OnlineOrder - Application starts successfully
⭐ Important Points
- Bean name = class name (camelCase by default)
- Use
@Qualifierwhen multiple beans exist
5️⃣ Solution 2: Dynamic Bean Selection using @Configuration
📌 Best approach for real projects
Step 1: Interface
public interface Order {
void createOrder();
}
Step 2: Implementations (NO @Component)
public class OnlineOrder implements Order {
public void createOrder() {
System.out.println("Created Online Order");
}
}
public class OfflineOrder implements Order {
public void createOrder() {
System.out.println("Created Offline Order");
}
}
Step 3: Configuration Class
@Configuration
public class OrderConfig {
@Bean
public Order createOrder(@Value("${isOnlineOrder}") boolean isOnlineOrder) {
if (isOnlineOrder) {
return new OnlineOrder();
} else {
return new OfflineOrder();
}
}
}
Step 4: application.properties
isOnlineOrder=false
✅ Output (From PDF – Page 2 Logs)
Created Offline Order
Change to:
isOnlineOrder=true
➡ Output:
Created Online Order
6️⃣ @Value Annotation (Important Concept)
🔹 What is @Value?
Used to inject values from:
application.properties- Environment variables
- Inline literals
✔ Example
@Value("${isOnlineOrder}")
boolean isOnlineOrder;
Inline Literal Example (From PDF)
@Bean
public Order createOrderBean(@Value("false") boolean isOnlineOrder) {
if (isOnlineOrder) {
return new OnlineOrder();
} else {
return new OfflineOrder();
}
}
7️⃣ Extra Points (Not Clearly Mentioned in PDF)
🔸 Why Dynamic Bean Initialization is Powerful
- Environment-based configuration
- No code changes needed
- Easy switching between implementations
- Ideal for microservices
🔸 Best Practices
- Prefer
@Configuration + @Beanfor logic-based creation - Use
@Qualifieronly when logic is simple - Avoid multiple
@Componentbeans of same type without control
8️⃣ Interview / Exam Questions & Answers
Q1. What is UnsatisfiedDependencyException?
Answer:
It occurs when Spring cannot resolve which bean to inject due to missing or multiple matching beans.
Q2. Difference between @Qualifier and @Primary?
Answer:
@Qualifier: Explicitly specifies bean name@Primary: Sets default bean when multiple beans exist
Q3. When should we use dynamic bean initialization?
Answer:
When bean selection depends on:
- Configuration
- Environment
- Runtime conditions
Q4. Can @Value inject default values?
Answer:
Yes
@Value("${isOnlineOrder:false}")
Q5. Which approach is better for enterprise apps?
Answer:
@Configuration + @Bean approach because it provides better control and flexibility.
9️⃣ One-Line Summary (Exam Gold ✨)
Dynamic Bean Initialization allows Spring Boot to decide bean creation at runtime using configuration and conditions, solving multiple implementation conflicts cleanly.
