🌱 Spring Boot – Bean and Its Lifecycle
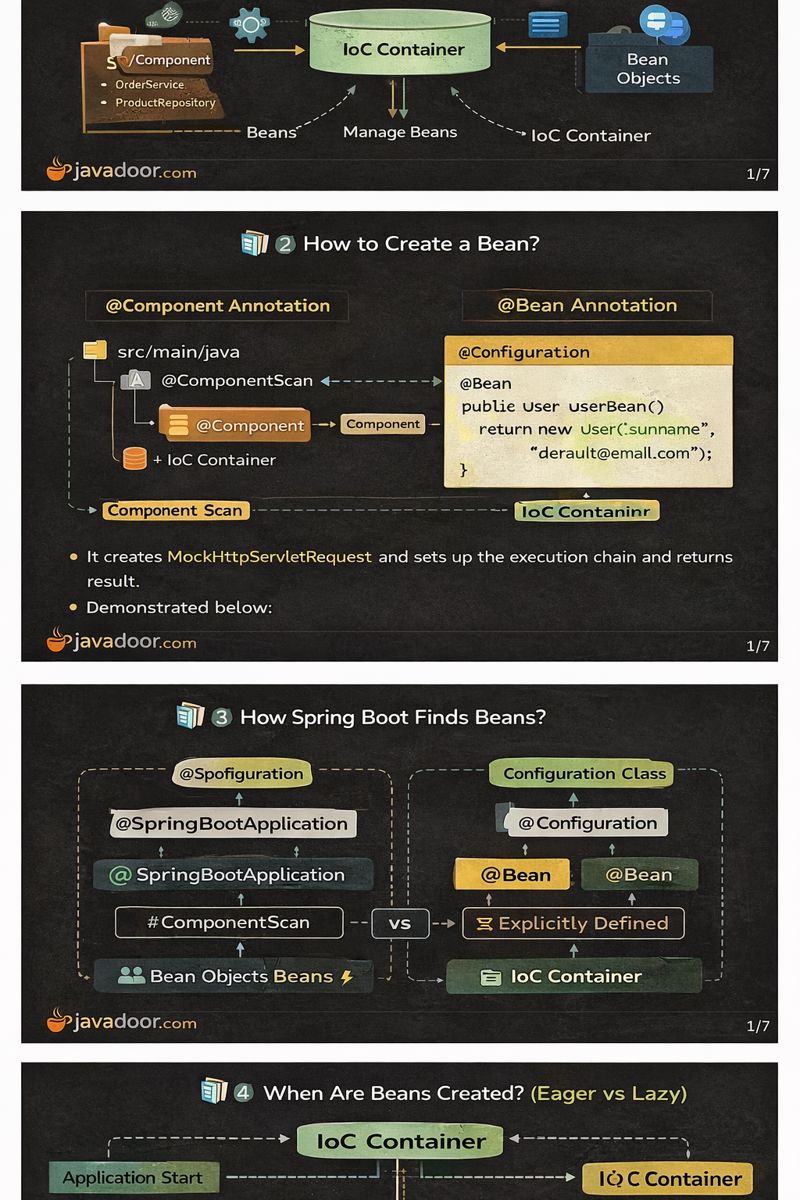
1️⃣ What is a Bean?
A Bean is a Java object that is created, managed, and destroyed by the Spring IoC (Inversion of Control) Container.
🔑 Key Points
- Beans are managed by the IoC Container
- The container handles:
- Instantiation
- Dependency Injection
- Lifecycle callbacks
- Destruction
🧠 Internal Working
- Spring scans the classpath
- Identifies bean definitions
- Creates bean instances
- Stores them in the ApplicationContext


✅ Quick Summary
- Bean = managed Java object
- Lifecycle controlled by Spring
- Core of Spring Framework
❓ Interview / Exam Questions (with Answers)
- What is a Spring Bean?
→ A Java object managed by the Spring IoC container. - Who manages the bean lifecycle?
→ Spring IoC Container. - Are all objects beans?
→ No, only objects created by Spring.
2️⃣ How to Create a Bean?
Spring provides two main approaches.
🔹 Approach 1: @Component Annotation
@Component
public class User {
private String username;
private String email;
}
🔸 Notes
- Follows Convention over Configuration
- Spring auto-detects via Component Scanning
- Related stereotypes:
- @Controller
- @Service
- @Repository


🔹 Approach 2: @Bean Annotation
Used when constructor parameters or custom logic are required.
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public User userBean() {
return new User("defaultUser", "default@email.com");
}
}
⚠️ Why @Bean is Needed?
If a class has a parameterized constructor, Spring does not know what values to pass automatically.

✅ Quick Summary
@Component→ auto creation@Bean→ manual configuration- Choose based on constructor needs
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- Difference between @Component and @Bean?
→ @Component is auto-scanned, @Bean is explicitly defined. - When should @Bean be preferred?
→ When constructor parameters are required. - Can we create multiple beans of same type?
→ Yes, via multiple @Bean methods.
3️⃣ How Spring Boot Finds Beans?
🔹 Method 1: Component Scanning
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example")
public class Application { }
- Scans base package & sub-packages
- Finds classes annotated with stereotypes
🔹 Method 2: Explicit Bean Definition
- Beans defined using
@Beaninside@Configuration


✅ Quick Summary
- Beans found via scanning or configuration
- Base package is critical
- Misplacement causes bean not found errors
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- What happens if a bean is outside base package?
→ It will not be detected. - What does @ComponentScan do?
→ Scans packages for beans. - Can @Bean work without component scan?
→ Yes.
4️⃣ When Are Beans Created? (Eager vs Lazy)
🔹 Eager Initialization (Default)
- Beans created at application startup
- Applies to Singleton scope
🔹 Lazy Initialization
- Beans created only when requested
- Enabled using
@Lazy
@Lazy
@Component
public class OrderService {
public OrderService() {
System.out.println("OrderService Initialized");
}
}


✅ Quick Summary
- Singleton → eager by default
- Lazy improves startup time
- Use carefully in production
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- Default bean initialization type?
→ Eager. - When is @Lazy used?
→ To delay bean creation. - Does @Lazy work with prototype?
→ Prototype beans are always lazy.
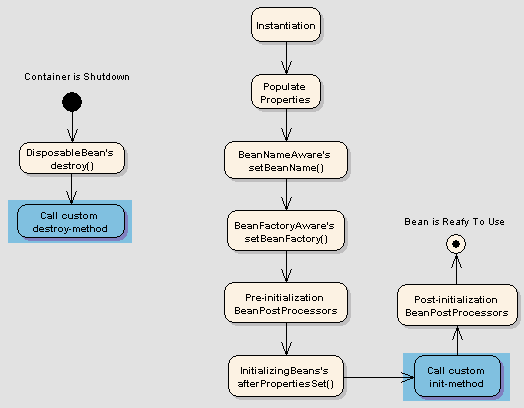
5️⃣ Lifecycle of a Spring Bean
🔄 Complete Lifecycle Steps
- Application Start
- IoC Container Created
- Bean Instantiated
- Dependencies Injected
- @PostConstruct
- Bean Ready for Use
- @PreDestroy
- Bean


🔹 Lifecycle Callback Example
@Component
public class User {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("Bean Initialized");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("Bean Destroyed");
}
}
🧠 Internal Working
@PostConstruct→ called after DI@PreDestroy→ called before container shutdown- Container shutdown occurs via:
context.close()- JVM shutdown hook
⚙️ Performance & Best Practices
- Avoid heavy logic in constructors
- Use
@PostConstructfor initialization - Release resources in
@PreDestroy - Prefer constructor injection
✅ Quick Summary
- Lifecycle is fully managed by Spring
- Hooks available for customization
- Critical for resource management
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- When is @PostConstruct executed?
→ After dependency injection. - Is @PreDestroy called for prototype beans?
→ No. - Who controls bean destruction?
→ IoC Container.
🎯 FINAL CONCLUSION
- Beans are the backbone of Spring
- Lifecycle understanding is frequently asked
- Correct usage prevents memory leaks and startup issues
