1️⃣ What is Maven?
Maven is a build automation and project management tool used primarily for Java and Spring Boot applications.
🎯 Problems Maven Solves
- Build generation (compile, test, package)
- Dependency resolution (automatic download & versioning)
- Standard project structure
- Plugin-based extensibility
- Reproducible builds
🧠 Core Concept
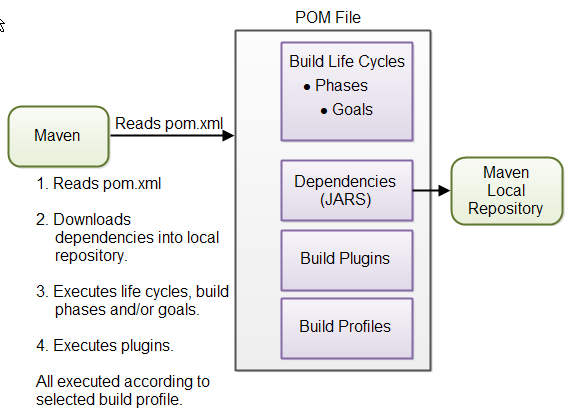
Maven is declarative, not procedural:
- You describe WHAT you want (in
pom.xml) - Maven decides HOW to do it (via lifecycle + plugins)


![]()
✅ Quick Summary
- Maven automates build + dependency management
- Uses pom.xml as a single source of truth
- Essential for Spring Boot & enterprise projects
❓ Interview / Exam Questions (with Answers)
- What is Maven?
→ A build and dependency management tool for Java projects. - Why is Maven declarative?
→ Developers define configuration, not execution steps. - What problem does Maven solve compared to Ant?
→ Dependency management and standard lifecycle.
2️⃣ pom.xml – Project Object Model
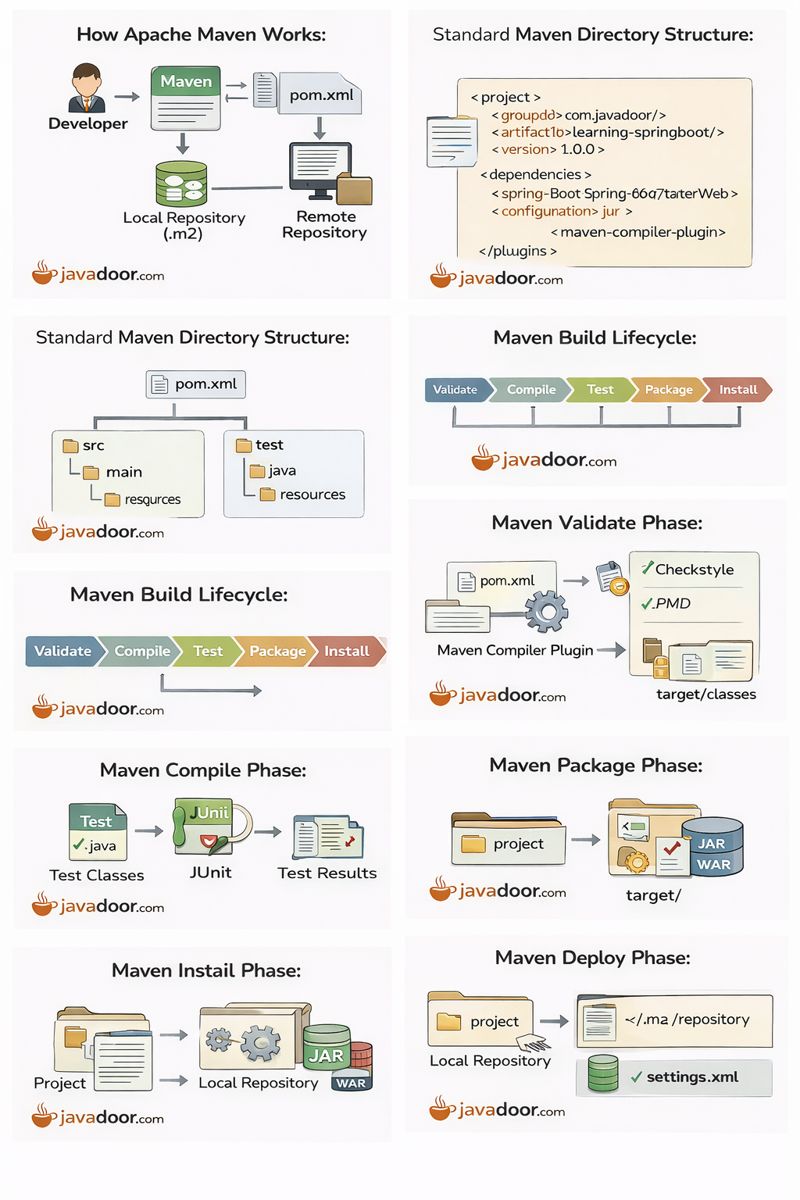
The pom.xml file is the heart of a Maven project.
🔹 Mandatory Project Coordinates
| Tag | Meaning |
|---|---|
| groupId | Organization / package namespace |
| artifactId | Project name |
| version | Build version |
| packaging | jar / war |
<project>
<groupId>com.javadoor</groupId>
<artifactId>learning-springboot</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
</project>
🔹 Dependency Management (Internal Working)
- Maven downloads dependencies from Maven Central
- Stores them in ~/.m2/repository
- Uses transitive dependencies automatically
⚠️ Edge Case:
Conflicting versions → solved using dependency mediation (nearest-wins).


✅ Quick Summary
pom.xmlcontrols dependencies, plugins, lifecycle- Enables reproducible builds
- Supports multi-module projects
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- What is pom.xml?
- How does Maven resolve version conflicts?
- What are transitive dependencies?
3️⃣ Maven Standard Project Structure
Maven enforces Convention over Configuration.
📁 Default Layout
project
├── pom.xml
└── src
├── main
│ ├── java
│ └── resources
└── test
└── java
🔍 Why This Matters
- IDEs auto-detect structure
- CI/CD pipelines rely on it
- Reduces onboarding time



✅ Quick Summary
- Enforced by Maven
- Separates production & test code
- Improves maintainability
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- Why does Maven enforce a directory structure?
- Where are compiled classes stored?
- Where are test cases placed?
4️⃣ Maven Build Lifecycle
Maven lifecycle = ordered phases executed sequentially.
🔁 Default Lifecycle Phases
| Order | Phase | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | validate | Validate project |
| 2 | compile | Compile source code |
| 3 | test | Run unit tests |
| 4 | package | Create JAR/WAR |
| 5 | verify | Quality checks |
| 6 | install | Local repo |
| 7 | deploy | Remote repo |
📌 Key Rule:
Running a later phase executes all previous phases automatically.



✅ Quick Summary
- Lifecycle is strictly ordered
- Prevents incomplete builds
- Core Maven concept for interviews
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- What happens when you run
mvn package? - Can phases be skipped?
- Difference between lifecycle and goal?
5️⃣ Validate Phase (mvn validate)
🔹 Purpose
- Ensures:
- Project structure is correct
- pom.xml is valid
- No compilation happens
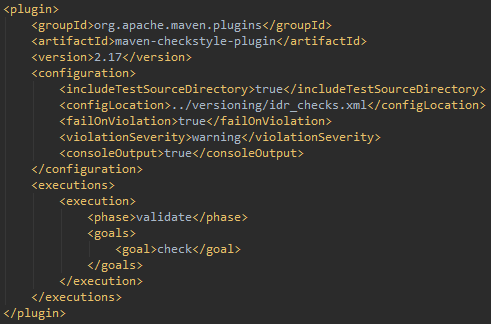
🔹 Real-World Use
- Enforce Checkstyle
- Enforce PMD rules
- Enforce license checks


✅ Quick Summary
- First lifecycle phase
- Ensures correctness before build
- Extensible using plugins
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- Does validate compile code?
- Why use validate phase?
- Can plugins run in validate?
6️⃣ Compile Phase (mvn compile)
🔹 What Happens Internally
- Uses maven-compiler-plugin
- Converts
.java→.class - Output stored in:
target/classes
⚙️ Performance Consideration
- Incremental compilation supported
- Faster in CI with dependency caching
🖼️ Required Diagram / Image
Type: Compilation Flow Diagram
Labels must contain:
- Source Code
- Compiler Plugin
- target/classes
Explains:
How Maven compiles Java code.



✅ Quick Summary
- Compiles only main code
- No tests executed
- Generates bytecode
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- Where does Maven store compiled classes?
- Which plugin compiles Java code?
- Does mvn compile run tests?
7️⃣ Test Phase (mvn test)
🔹 Purpose
- Executes unit tests
- Uses:
- JUnit
- TestNG
- Stops build if any test fails
🧠 Edge Case
- Integration tests are NOT run here (handled separately)
🖼️ Required Diagram / Image
Type: Testing Flow Diagram
Labels must contain:
- Test Classes
- JUnit
- Test Results
Explains:
How Maven executes unit tests.



✅ Quick Summary
- Ensures code correctness
- Mandatory for CI pipelines
- Build fails on test failure
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- What happens if a test fails?
- Which tests run in mvn test?
- Difference between test and verify?
8️⃣ Package Phase (mvn package)
🔹 Purpose
- Creates JAR / WAR
- Combines:
- Compiled code
- Resources
- Metadata
📦 Output Location
target/*.jar
🖼️ Required Diagram / Image
Type: Packaging Diagram
Labels must contain:
- Compiled Classes
- Resources
- JAR/WAR
Explains:
How Maven builds deployable artifacts.



✅ Quick Summary
- Produces final artifact
- Used in deployment pipelines
- Executes previous phases automatically
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- What is created in mvn package?
- Difference between jar and war?
- Where is the package stored?
9️⃣ Install Phase (mvn install)
🔹 Purpose
- Installs artifact into local repository
~/.m2/repository
🔹 Why Important
- Enables multi-module projects
- Allows reuse across local builds
🖼️ Required Diagram / Image
Type: Repository Diagram
Labels must contain:
- Project
- Local Repository
- Installed Artifact
Explains:
How Maven installs artifacts locally.


✅ Quick Summary
- Makes artifact reusable
- Local-only operation
- Required before deploy
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- Where does mvn install store artifacts?
- Why is install required before deploy?
- What is local repository?
🔟 Deploy Phase (mvn deploy)
🔹 Purpose
- Uploads artifact to remote repository
- Nexus
- Artifactory
- Maven Central
🔐 Configuration
- Repository in
pom.xml - Credentials in
settings.xml
🖼️ Required Diagram / Image
Type: Deployment Architecture Diagram
Labels must contain:
- Local Repository
- Remote Repository
- pom.xml
- settings.xml
Explains:
How Maven deploys artifacts to remote repositories.
![]()


✅ Quick Summary
- Final lifecycle phase
- Used in enterprise CI/CD
- Publishes artifacts
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- Difference between install and deploy?
- Where are credentials stored?
- Can deploy run without install?
🎯 FINAL CONCLUSION
- Maven is mandatory knowledge for Spring Boot
- Lifecycle understanding is frequently tested
- pom.xml mastery separates junior vs senior engineers
If you want next:
- ✅ PDF export
- ✅ Microservices-specific Maven notes
- ✅ Interview cheat sheet (1-page)
- ✅ CI/CD Maven pipeline explanation
Just tell me.
