🌱 Spring Boot – Dependency Injection (DI)
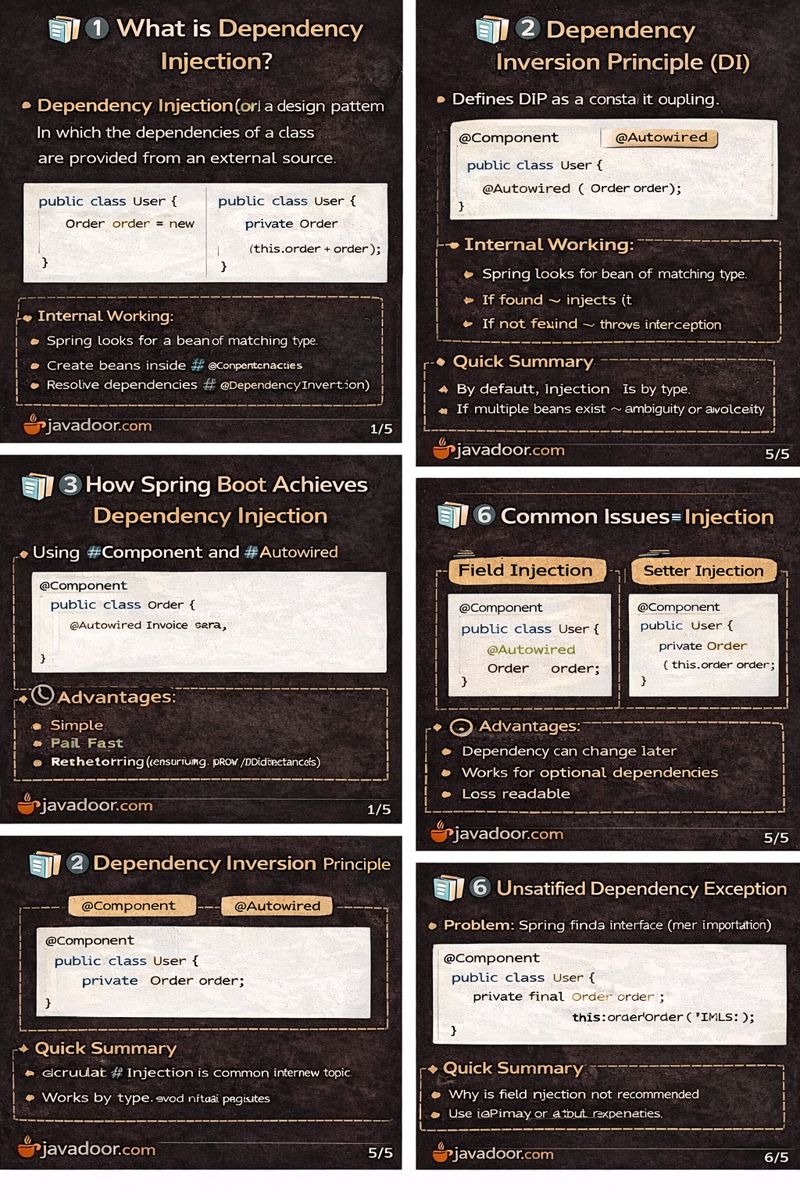
1️⃣ What is Dependency Injection?
Dependency Injection (DI) is a design pattern in which the dependencies of a class are provided from an external source instead of the class creating them itself.
🔑 Key Idea
- A class should be independent of how its dependencies are created
- Dependencies are injected by the Spring IoC Container
❌ Problem Without Dependency Injection (From PDF)
public class User {
Order order = new Order(); // tight coupling
}
Issues:
- Tight Coupling
Useris directly dependent onOrder
- Hard to Change Implementation
- If
Orderlogic changes →Usermust change
- If
- Violates SOLID Principle
- Breaks Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
✅ With Dependency Injection
public class User {
private Order order;
public User(Order order) {
this.order = order;
}
}
✔ Now User depends on abstraction, not implementation.
🧠 Internal Working (Spring Boot)
- Spring scans classes annotated with
@Component - Creates beans inside IoC Container
- Resolves dependencies
- Injects required beans automatically
✅ Quick Summary
- DI removes tight coupling
- Makes code flexible and testable
- Core feature of Spring Framework
❓ Interview / Exam Questions (with Answers)
- What is Dependency Injection?
→ Providing dependencies from outside instead of creating them inside the class. - Which SOLID principle is related to DI?
→ Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP). - Who performs DI in Spring Boot?
→ Spring IoC Container.
2️⃣ Dependency Inversion Principle (DIP)
🔹 Definition
High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules.
Both should depend on abstractions.
❌ Violating DIP (From PDF)
public class User {
OnlineOrder order = new OnlineOrder();
}
- Direct dependency on concrete class
- Not extensible
✅ Following DIP
public interface Order {}
public class OnlineOrder implements Order {}
public class User {
Order order;
public User(Order order) {
this.order = order;
}
}
✔ Code depends on interface, not implementation.
✅ Quick Summary
- DIP is part of SOLID
- DI is the implementation of DIP
- Promotes loose coupling
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- Difference between DI and DIP?
→ DIP is a principle, DI is its implementation. - Why is DIP important?
→ Improves flexibility and maintainability. - Can DI exist without interfaces?
→ Technically yes, but not recommended.
3️⃣ How Spring Boot Achieves Dependency Injection
🔹 Using @Component and @Autowired
@Component
public class Order {}
@Component
public class User {
@Autowired
Order order;
}
🔹 How @Autowired Works Internally
- Spring looks for a bean of matching type
- If found → injects it
- If not found → throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
⚠️ Important Notes
- By default, injection is by type
- If multiple beans exist → ambiguity error
✅ Quick Summary
@Autowiredinjects dependencies- Works by type
- Managed by IoC Container
❓ Interview / Exam Questions
- What happens if multiple beans of same type exist?
→ NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException. - Can @Autowired work without @Component?
→ No, bean must exist. - Is @Autowired mandatory?
→ Not always (constructor injection).
4️⃣ Types of Dependency Injection (Very Important)
4.1 Field Injection
@Component
public class User {
@Autowired
private Order order;
}
🔹 Internal Mechanism
- Uses reflection
- Injects dependency after object creation
✅ Advantages
- Simple
- Less code
❌ Disadvantages (From PDF + Extra)
- Cannot use
final - Hard to test
- Risk of NullPointerException
- Not recommended in production
✅ Quick Summary
- Field injection is easy
- Poor testability
- Avoid in real projects
❓ Interview Questions
- Why is field injection not recommended?
→ Poor testability and hidden dependencies. - Does field injection support immutability?
→ No. - How does Spring inject fields?
→ Using reflection.
4.2 Setter Injection
@Component
public class User {
private Order order;
@Autowired
public void setOrder(Order order) {
this.order = order;
}
}
✅ Advantages
- Dependency can be changed later
- Useful for optional dependencies
❌ Disadvantages
- Object may be in incomplete state
- Less readable
✅ Quick Summary
- Setter injection allows flexibility
- Not ideal for mandatory dependencies
❓ Interview Questions
- When should setter injection be used?
→ For optional dependencies. - Can setter injection ensure immutability?
→ No. - Is setter injection thread-safe?
→ No guarantee.
4.3 Constructor Injection (Recommended)
@Component
public class User {
private final Order order;
public User(Order order) {
this.order = order;
}
}
🔹 Important Spring Boot Rule (From PDF)
- If only one constructor exists,
@Autowiredis not mandatory
✅ Advantages (From PDF + Extra)
- Ensures all dependencies are available at creation time
- Supports immutability
- Prevents NullPointerException
- Makes unit testing easy
- Fail-fast mechanism
❌ Disadvantages
- Constructor can become large (many dependencies)
✅ Quick Summary
- Best and recommended approach
- Mandatory dependencies only
- Preferred in interviews
❓ Interview Questions
- Why is constructor injection preferred?
→ Ensures immutability and fail-fast. - Is @Autowired mandatory on constructor?
→ No (single constructor). - Which injection is best for testing?
→ Constructor injection.
5️⃣ Common Issues in Dependency Injection
5.1 Circular Dependency (From PDF)
@Component
class Order {
@Autowired
Invoice invoice;
}
@Component
class Invoice {
@Autowired
Order order;
}
❌ Application fails to start.
🔹 Solutions
- Refactor code (best)
- Use
@Lazy - Use
@PostConstruct
5.2 @Lazy Injection
@Autowired
@Lazy
private Invoice invoice;
- Spring creates a proxy
- Actual object created only when needed
5.3 @PostConstruct Solution
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
invoice.setOrder(this);
}
✅ Quick Summary
- Circular dependency is common interview topic
- Refactoring is best solution
- @Lazy is workaround
❓ Interview Questions
- What is circular dependency?
→ Two beans depend on each other. - Best way to solve it?
→ Refactor code. - Does constructor injection allow circular dependency?
→ No.
6️⃣ Unsatisfied Dependency Exception
🔹 Problem
- Spring finds interface
- Multiple implementations exist
public interface Order {}
@Component
class OnlineOrder implements Order {}
@Component
class OfflineOrder implements Order {}
🔹 Solutions
1️⃣ @Primary
@Primary
@Component
class OnlineOrder implements Order {}
2️⃣ @Qualifier
@Autowired
@Qualifier("onlineOrder")
private Order order;
✅ Quick Summary
- Occurs when multiple beans exist
- Use @Primary or @Qualifier
❓ Interview Questions
- Difference between @Primary and @Qualifier?
→ @Primary sets default, @Qualifier is explicit. - Which has higher priority?
→ @Qualifier. - Can both be used together?
→ Yes.
🎯 FINAL INTERVIEW TAKEAWAYS
- Dependency Injection is core to Spring
- Constructor Injection is best practice
- Circular dependency & Unsatisfied dependency are must-know
- DI improves testability, scalability, maintainability
